E-Commerce Giants: A SWOT Analysis of Alibaba
In the rapidly evolving world of e-commerce, few players have left as profound an impact as Alibaba. Founded in 1999 by Jack Ma, this Chinese multinational conglomerate has emerged as a global giant in the digital marketplace, providing a platform for businesses and consumers alike. With its diverse range of services, including e-commerce, cloud computing, digital payments, and more, Alibaba has become a force to be reckoned with. In this article, we will conduct a comprehensive SWOT analysis of Alibaba, evaluating its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
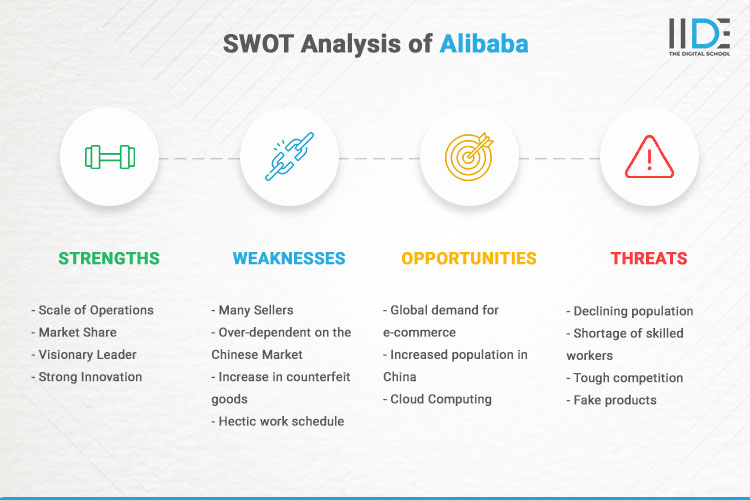
Strengths:
Vast Market Presence: Alibaba enjoys a massive market presence both in China and internationally. With its flagship platform, Alibaba.com, serving as a business-to-business (B2B) marketplace connecting global suppliers and buyers, and its consumer-facing platforms like Taobao and Tmall, the company has created a strong ecosystem that caters to diverse customer segments.
Diverse Business Ecosystem: One of Alibaba’s key strengths lies in its diversified business ecosystem. Beyond e-commerce, the company has expanded its operations to cloud computing, digital entertainment, logistics, and financial services. This diversification not only mitigates risk but also allows the company to capitalize on cross-selling and up-selling opportunities.
Innovative Technology and AI Integration: Alibaba heavily invests in research and development, focusing on cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and machine learning. These technologies drive data-driven decision-making, enhance customer experience, and optimize supply chain operations.
Strong Financial Performance: The company’s financial performance is a testament to its strength. Alibaba has consistently reported robust revenue growth and profitability. Its strong financial position enables the company to invest in strategic acquisitions and global expansion.
Dominance in Emerging Markets: Alibaba has successfully established a foothold in high-potential markets like Southeast Asia and India. Through strategic investments in local e-commerce platforms and partnerships with local players, Alibaba has gained significant market share in these regions.
Weaknesses:
Counterfeit Concerns: One of Alibaba’s persistent challenges has been the prevalence of counterfeit products on its platforms. Despite efforts to combat this issue, the company continues to face criticism from brands and regulators regarding the effectiveness of its anti-counterfeit measures.
Dependence on Chinese Market: While Alibaba has expanded its international presence, it still heavily relies on the Chinese market for a substantial portion of its revenue. This dependence on a single market exposes the company to geopolitical and regulatory risks specific to China.
Logistics and Supply Chain Complexity: The vast scale of Alibaba’s operations brings inherent logistical challenges. The company must continuously optimize its supply chain to maintain efficiency and meet growing customer expectations, both domestically and internationally.
Competition from Rivals: Alibaba operates in a fiercely competitive industry, facing competition not only from domestic rivals like JD.com but also from global players like Amazon and eBay. This competition puts pressure on the company to innovate constantly and offer compelling services to retain its customer base.
Opportunities:
International Expansion: As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, Alibaba has the opportunity to further expand its international presence. By tapping into emerging markets and fostering partnerships with local players, the company can access new customer segments and reduce its reliance on the Chinese market.
Diversification into New Sectors: Alibaba’s foray into various sectors, such as cloud computing and digital payments, has shown promise. Expanding its presence in these areas and exploring new ventures aligned with its core strengths can open up additional revenue streams.
Growth of Mobile Commerce: With the proliferation of smartphones and increasing internet penetration, mobile commerce is on the rise. Alibaba’s strong mobile applications and payment platforms, like Alipay, position the company well to capitalize on this growing trend.
Integration of Blockchain Technology: Alibaba has already made strides in exploring blockchain technology for enhancing supply chain transparency and security. Further integration of blockchain could improve trust and efficiency in the e-commerce ecosystem.
Threats:
Regulatory Challenges: The e-commerce industry is subject to evolving regulations and policies, both domestically and internationally. Regulatory changes can impact Alibaba’s operations and may result in compliance challenges or legal issues.
Geopolitical Tensions: As a multinational company, Alibaba is vulnerable to geopolitical tensions between China and other countries. Trade disputes or political conflicts may disrupt its global operations and expansion plans.
Cybersecurity Risks: With its vast online presence, Alibaba faces cybersecurity threats from hackers and data breaches. A significant security breach could damage its reputation and erode customer trust.
Changing Consumer Preferences: Consumer preferences and shopping behaviors are constantly evolving. Alibaba must stay attuned to these changes and adapt its strategies to meet the ever-changing demands of its customers.
In conclusion, Alibaba has undoubtedly achieved remarkable success as an e-commerce giant, but it is not without its challenges. Conducting a SWOT analysis provides valuable insights into the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, enabling it to make informed decisions and capitalize on its advantages. As the global e-commerce landscape continues to evolve, Alibaba’s ability to innovate, expand internationally, and address its weaknesses will be critical in maintaining its position as a dominant player in the industry.




